Ruby Hall Clinic stands at the forefront of Interventional Radiology in Pune, offering cutting-edge, minimally invasive treatments that blend advanced imaging with surgical precision. Our dedicated Interventional Radiology Department is the first of its kind in Pune, equipped with the city’s inaugural Bi-Plane Cath Lab and recognised by MUHS for offering 2 Fellowship seats in Interventional Radiology.
What is Interventional Radiology?
Interventional Radiology (IR) is a modern medical specialty that utilizes imaging modalities like CT, ultrasound and DSA to guide minimally invasive procedures. These techniques allow for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatments, often replacing the need for traditional surgery.

This minimally invasive procedure uses real-time imaging—either CT or ultrasound—to guide a fine needle precisely into a lesion for tissue sampling. It significantly reduces the risk compared to conventional biopsies and is also used for safe and effective drainage of fluid or pus collections in the body, avoiding the need for open surgery.
Angiography is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize blood flow in arteries. In peripheral arterial disease (PAD), it helps to identify blockages or narrowing. Angioplasty follows, using a balloon catheter to widen affected arteries, often followed by stenting to maintain blood flow and prevent re-narrowing.
This life-saving procedure blocks abnormal or bleeding blood vessels using materials such as coils or glue. It’s particularly useful in managing acute bleeding (like gastrointestinal or traumatic haemorrhages) and can also treat vascular tumours or malformations by cutting off their blood supply.
In this advanced cancer therapy, chemotherapy drugs are delivered directly to the tumour through its feeding artery. The technique maximises drug concentration at the tumour site while minimising systemic side effects. It’s primarily used in non-surgical liver cancer cases.
Radioembolisation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat liver tumours by delivering radiation directly to the tumour cells through tiny, radioactive beads called microspheres. These microspheres are injected into the blood vessels supplying the tumour, where they become trapped and release radiation, killing cancer cells and shrinking the tumour.
Thermal ablation is a minimally invasive technique where a needle-like probe delivers extreme heat or cold to destroy cancerous tissue. Guided by imaging, it’s especially effective for treating small liver tumours or metastases when surgery isn’t feasible.



Laser ablation uses concentrated light energy to close off faulty veins, improving circulation and cosmetic appearance without the need for surgery.
RFA delivers thermal energy through a catheter to collapse diseased veins. It’s minimally invasive and ideal for treating larger varicose veins.
In this treatment, a sclerosant solution is injected into small veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time. It’s simple, quick and virtually painless.
MOCA combines mechanical irritation of the vein with a chemical sclerosant, offering an effective, heat-free option for patients with superficial vein issues.
A medical-grade adhesive is used to seal the diseased vein shut. This technique avoids the need for heat or tumescent anaesthesia, providing excellent patient comfort.
RFA targets tumours with localised heat via a needle electrode, offering a precise, outpatient treatment option for liver, kidney or lung cancers.
TACE delivers chemotherapy directly into the tumour’s blood supply while blocking it, intensifying the drug’s effect and reducing systemic exposure.
Tiny radioactive beads are injected into the tumour’s blood supply, delivering high-dose radiation to cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
This technique generates electromagnetic waves to heat and destroy tumour cells. It’s efficient for larger tumours in organs like the liver or lungs.
IRE uses electrical pulses to disrupt cancer cell membranes without heating. It’s especially valuable near critical structures where thermal damage must be avoided.
Cryoablation is a procedure that uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissue, used to treat various cancers and other conditions. It involves inserting a cryoprobe into the affected area, which is then cooled to freezing temperatures to kill the targeted cells
Performed before tumour surgery, this reduces blood supply to the mass, making surgical removal safer and less prone to bleeding.
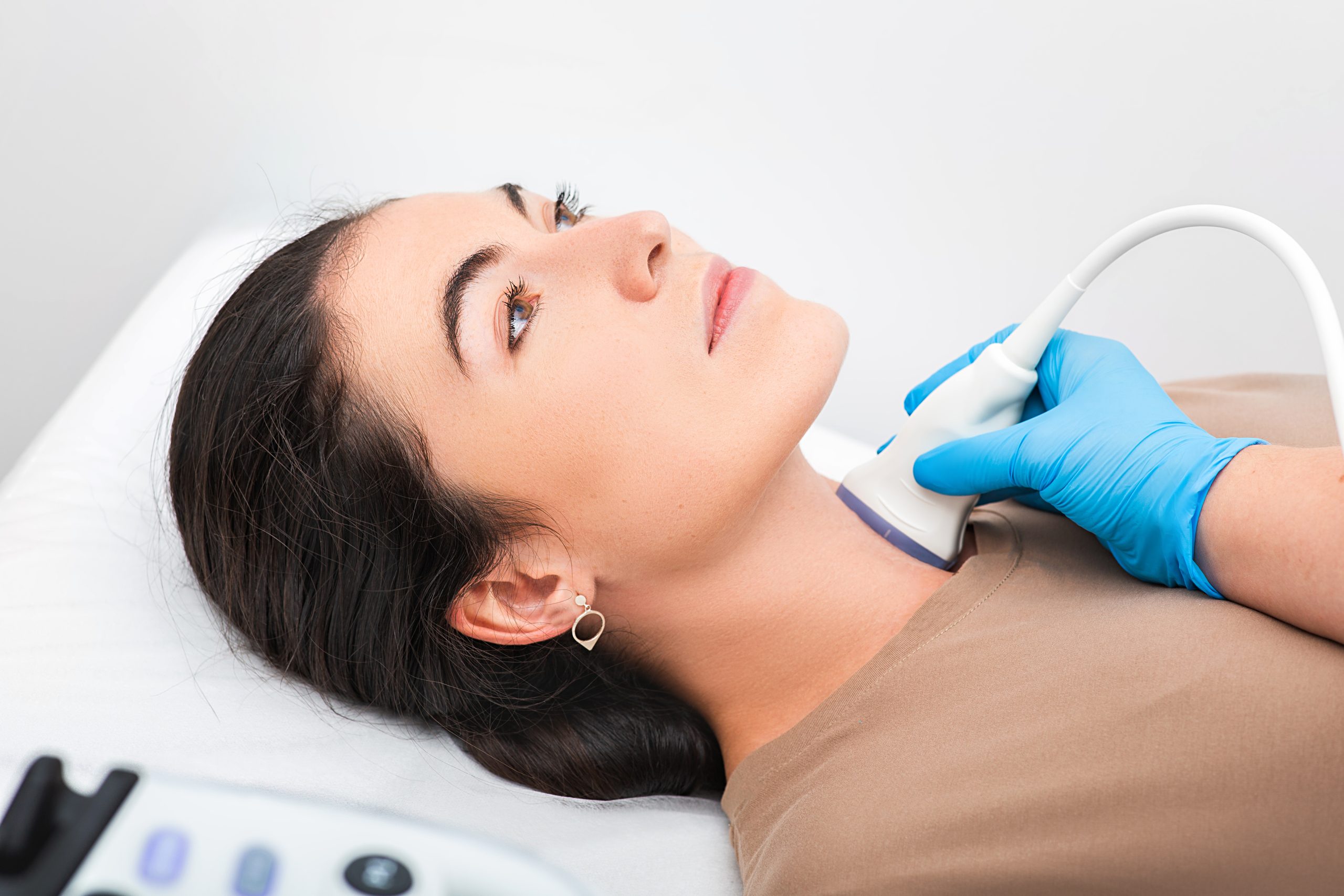
Benign thyroid nodules can be treated non-surgically with minimally invasive treatments like Microwave ablation, RFA, Ethanol ablation and percutaneous trans-arterial embolisation.

Transrectal ultrasound guided biopsy of prostate is done to diagnose various conditions affecting prostate like prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, infection etc.
This is a minimally invasive nonsurgical treatment to shrink enlarged prostate gland and alleviate patient’s urinary symptoms like incomplete emptying, frequency, intermittency, urgency, weak stream, straining and nocturia.
There are nonsurgical minimally invasive image guided procedures done to relieve urinary tract obstructions.
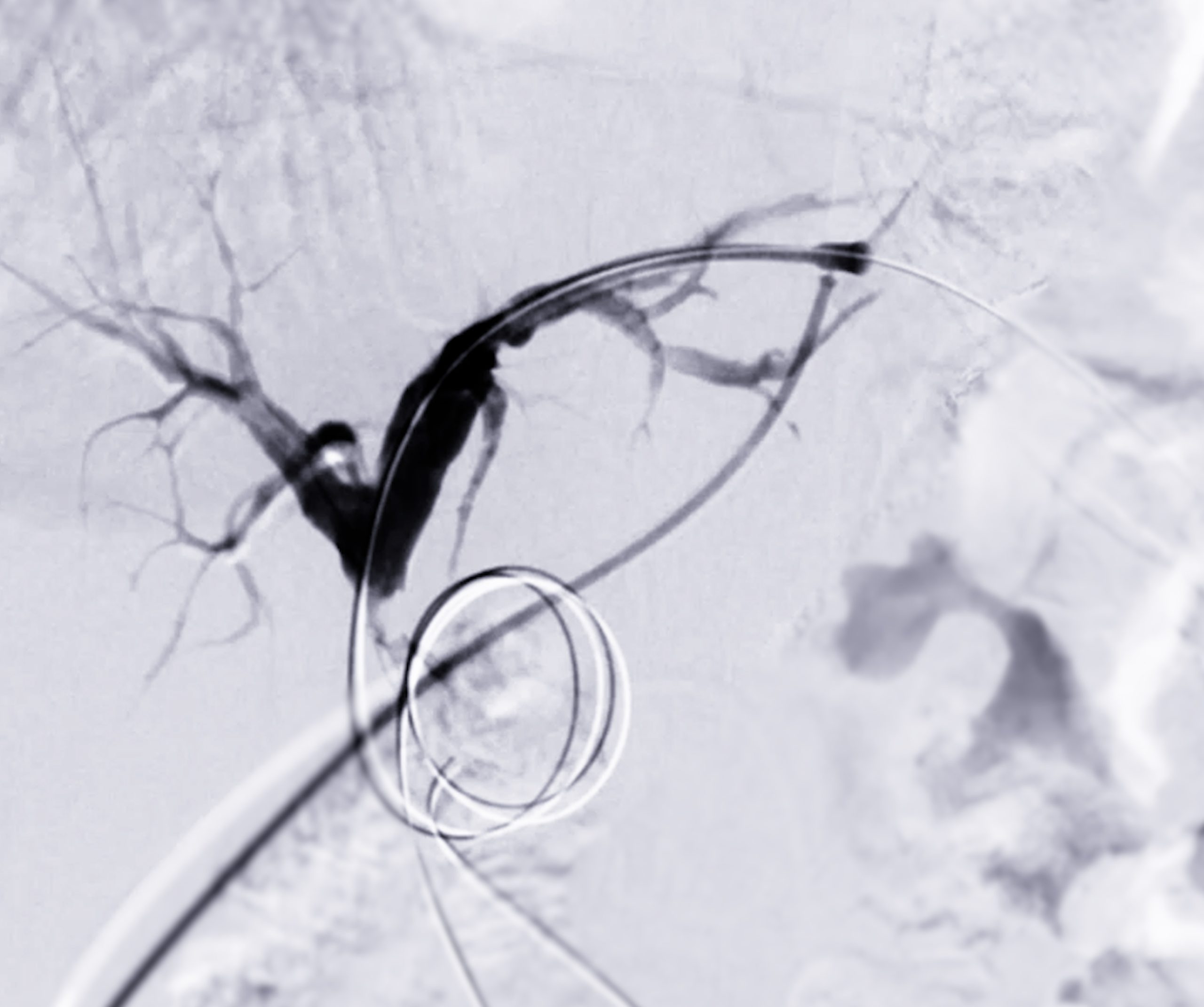
These treatments focus on diseases of the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. Biliary drainage and stenting can relieve blockages, while trans-jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) helps to manage portal hypertension.
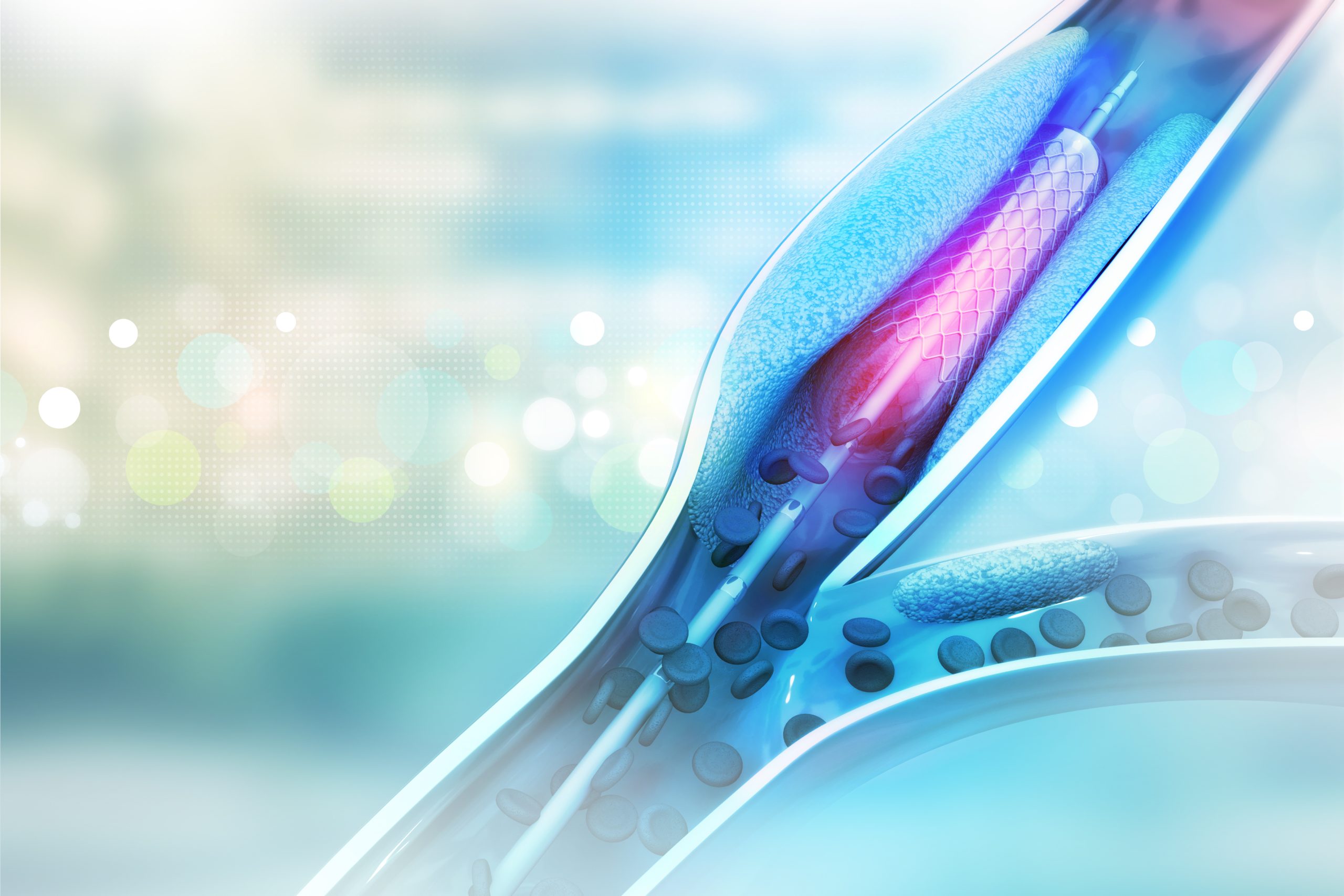
This restores blood flow by inflating a small balloon inside narrowed arteries and placing a stent to keep them open, relieving limb pain and preventing complications.
CDT delivers clot-dissolving medications directly into a blocked artery, targeting clots effectively while preserving healthy vessels.
A minimally invasive method to physically remove blood clots/atherosclerotic plaques from arteries, restoring circulation quickly in cases of acute blockage.
This targeted treatment dissolves clots in deep veins using medication delivered through a catheter, helping to prevent long-term damage.
Used to extract large or resistant clots, this procedure mechanically removes the blockage, often paired with thrombolytic drugs.
An IVC filter is inserted to trap clots traveling from the legs to the lungs, protecting against potentially fatal pulmonary embolisms.
A permcath provides long-term dialysis access for patients, placed through a minimally invasive technique with quick recovery.
When a dialysis fistula becomes narrowed, angioplasty can restore its function without the need for new surgical creation.
Used to open narrowed central veins and improve blood flow, ensuring efficient dialysis access in patients with previous line placements.
This allows patients to undergo home-based peritoneal dialysis through a small, tunnelled catheter placed with image guidance.
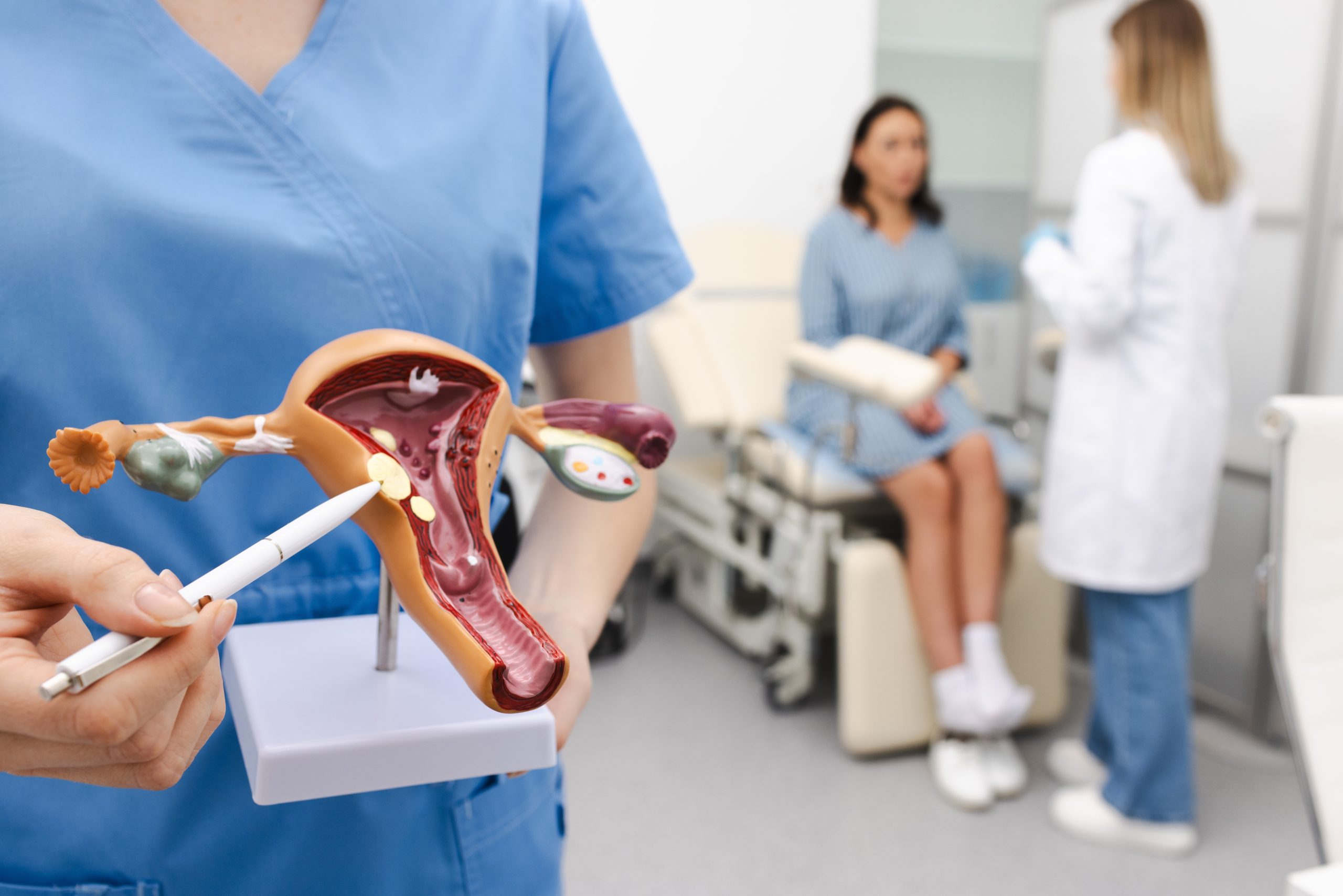
This procedure involves blocking blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink and relieve symptoms such as pain or heavy bleeding, without the need for surgery.
RFA (Radiofrequency Ablation), Microwave ablation of fibroids can be done causing them to shrink and relieve symptoms such as pain or heavy bleeding, without the need for surgery.
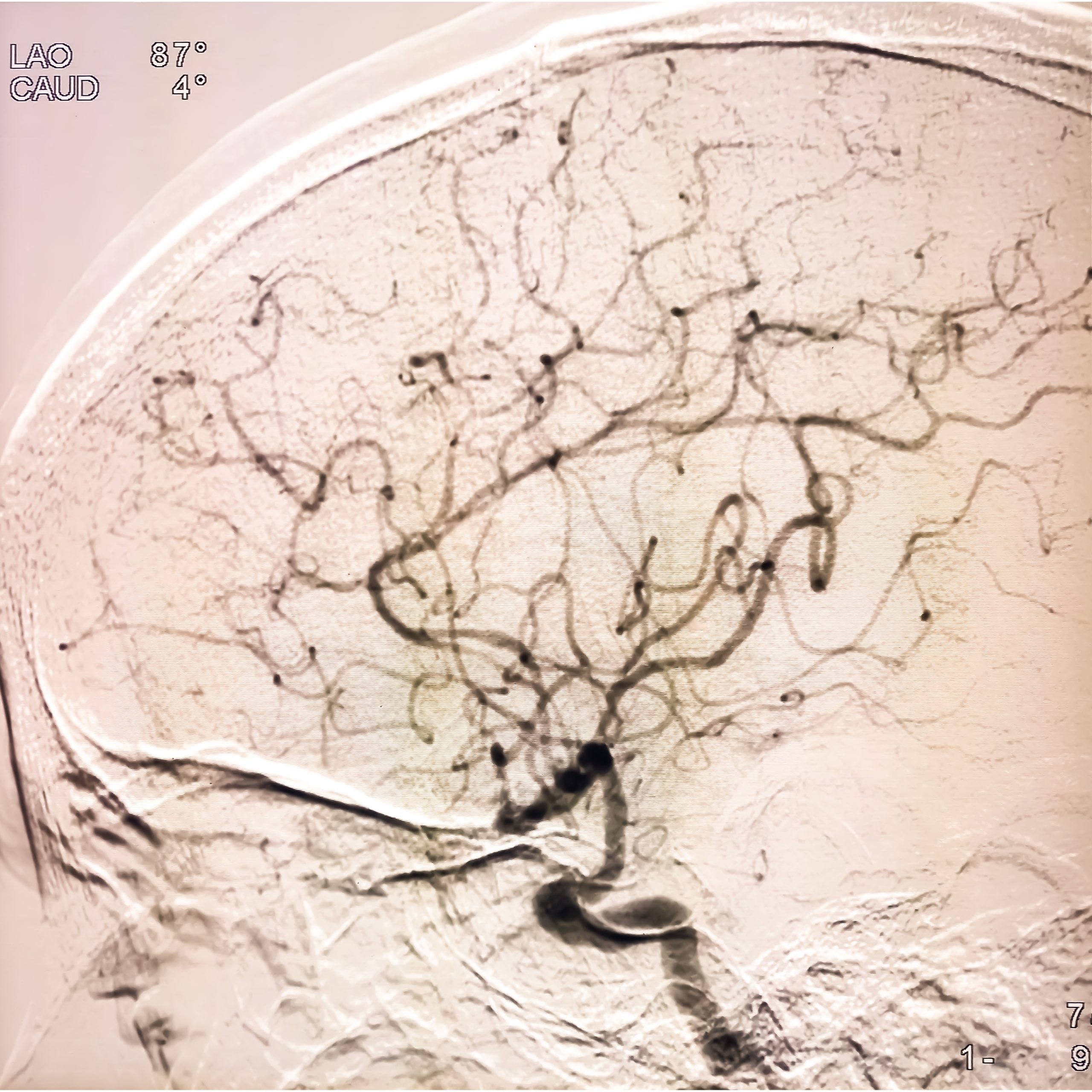
DSA of the brain is used to visualise the blood vessels in the brain, similar to a heart angiogram and is used for diagnosing and treating various brain vascular problems, including aneurysms, stroke and vascular malformations.
Interventions for stroke include both acute event and long-term management depending on the type and severity of stroke.
Acute interventions focus on restoring blood flow which includes Mechanical Thrombectomy (MT) or intra-arterial thrombolysis.
Long term management of stroke involves procedures that aim at improving blood flow to the affected part of the brain like intracranial angioplasty and stenting as well as procedures that prevent future strokes such as carotid stenting.
Carotid stenting is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat narrowing (stenosis) in the carotid arteries that prevents future strokes. This procedure is an alternative to surgical procedures like carotid endarterectomy, especially in patients who are at high risk for surgery.
Conditions like AV malformations, aneurysms, AV-fistulas (dural AVF, pial AVF, carotid-cavernous fistula), spinal AV malformations / AV fistulas can be treated via minimally invasive approaches that are alternative to open neurosurgical procedures.
Pre-operative embolisations for various tumours like meningioma, vertebral haemangioma, carotid body tumour, juvenile naso-pharyngeal angiofibroma (JNA) can be done as an adjunct to surgery which helps to reduce the intra-operative blood loss.
Intracranial aneurysms can be treated with minimally invasive procedures such as endovascular coiling / stenting / flow diverter placement.
Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (CDT) and Catheter-Assisted Thrombectomy can be done via minimally invasive accesses
Cortical venous sinus stenting can also be done for Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) that causes refractory headache that does not reduce with medical management.
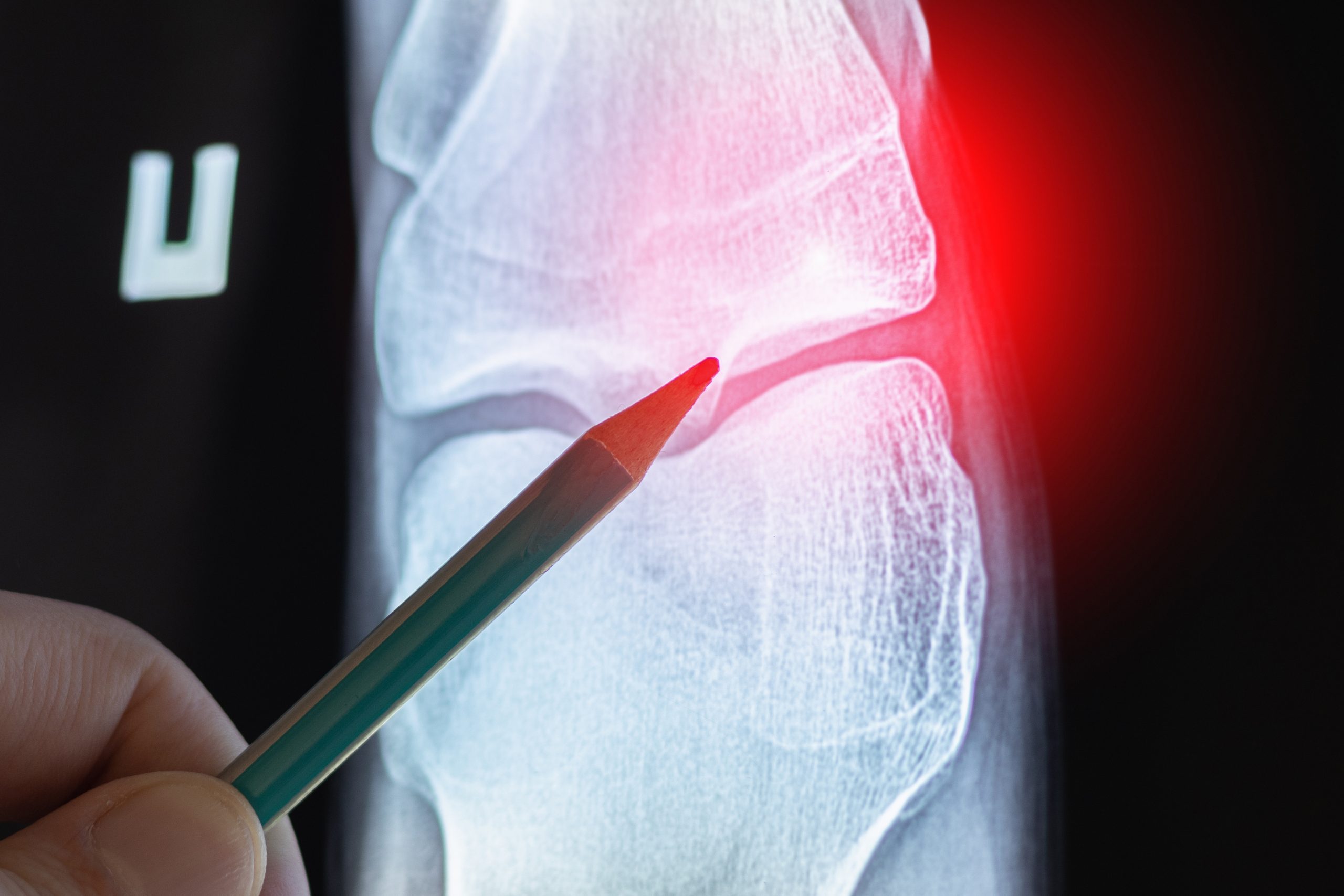
This benign bone tumour can be treated non-surgically by RFA (Radio frequency Ablation) or Microwave or Cryoablation.
Genicular artery embolisation (GAE) is a minimally invasive procedure that reduces pain in knee osteoarthritis by blocking blood flow to the inflamed synovium, the lining of the knee joint. It’s an alternative to surgery for some patients with knee pain.
Ultrasound and CT guided Fluid aspiration from various joints can be done as diagnostic and as therapeutic purposes.
Image guided steroid/anaesthetic drugs can be injected for relief from joint pains.
These are injections of steroids / anaesthetic drugs used for pain relief by targeting specific spinal nerve roots.
Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting bone cement into fractured vertebrae, providing pain relief and stabilising fractures caused by osteoporosis.
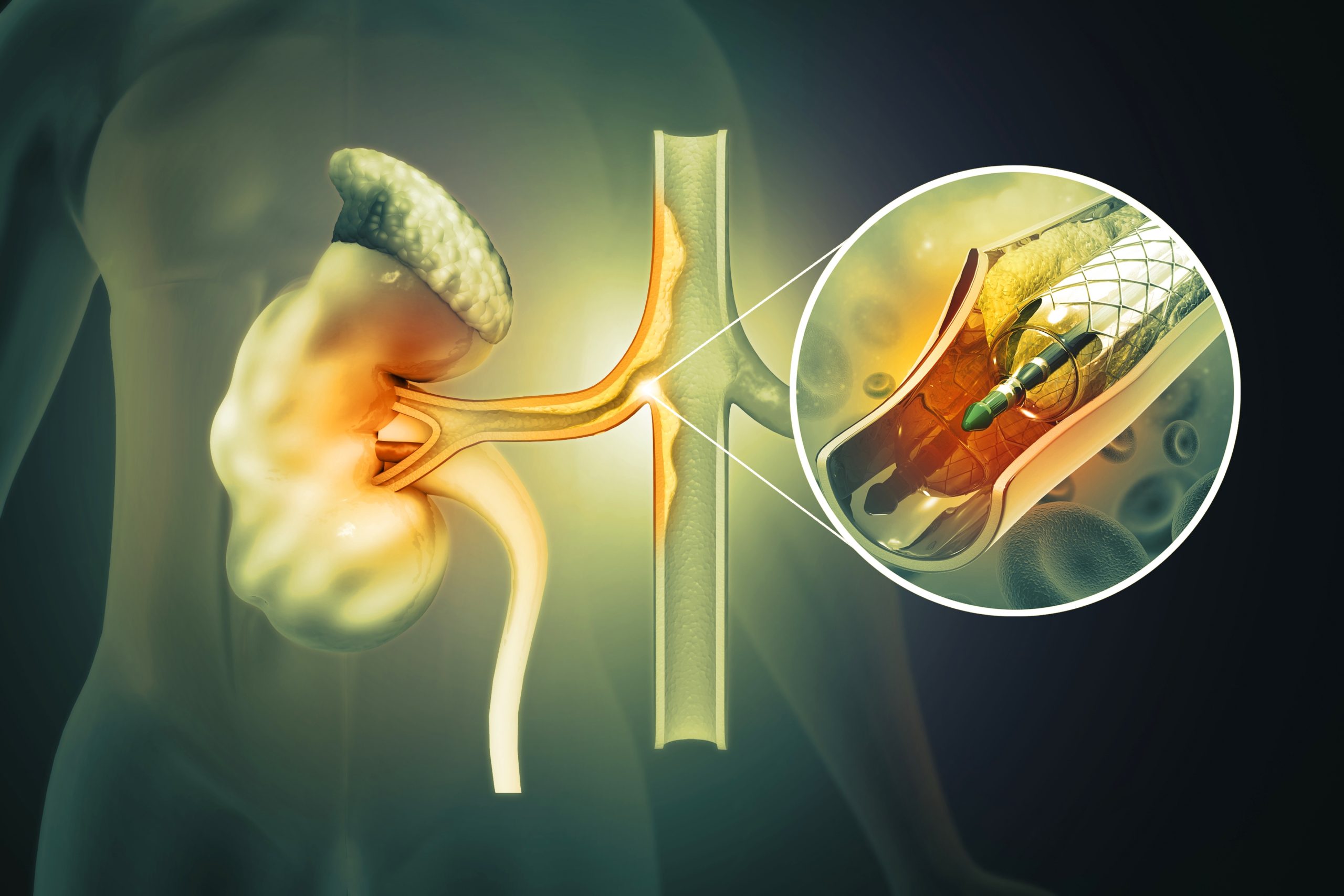
Renal artery stenting is performed to widen narrowed or blocked renal arteries, improving blood flow to the kidneys and preventing kidney damage, often used in cases of hypertension or renal artery stenosis.
This precise treatment delivers clot-busting drugs directly into pulmonary arteries, improving oxygenation and reducing strain on the heart.
Thrombectomy involves physically removing the clot from lung arteries, often used in massive or high-risk pulmonary embolism for rapid relief.
TIPSS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) is a procedure that creates a bypass between the portal and hepatic veins to manage portal hypertension, often used in Budd Chiari Syndrome to reduce complications like ascites.
Interventional procedures like tubal recanalisation, hysterosalpingography (HSG), and varicocele embolisation treat infertility by improving reproductive organ function without the need for surgery.
Repair of an aortic aneurysm often involves endovascular stenting or open surgery. These procedures restore the vessel’s integrity and prevent life-threatening rupture.
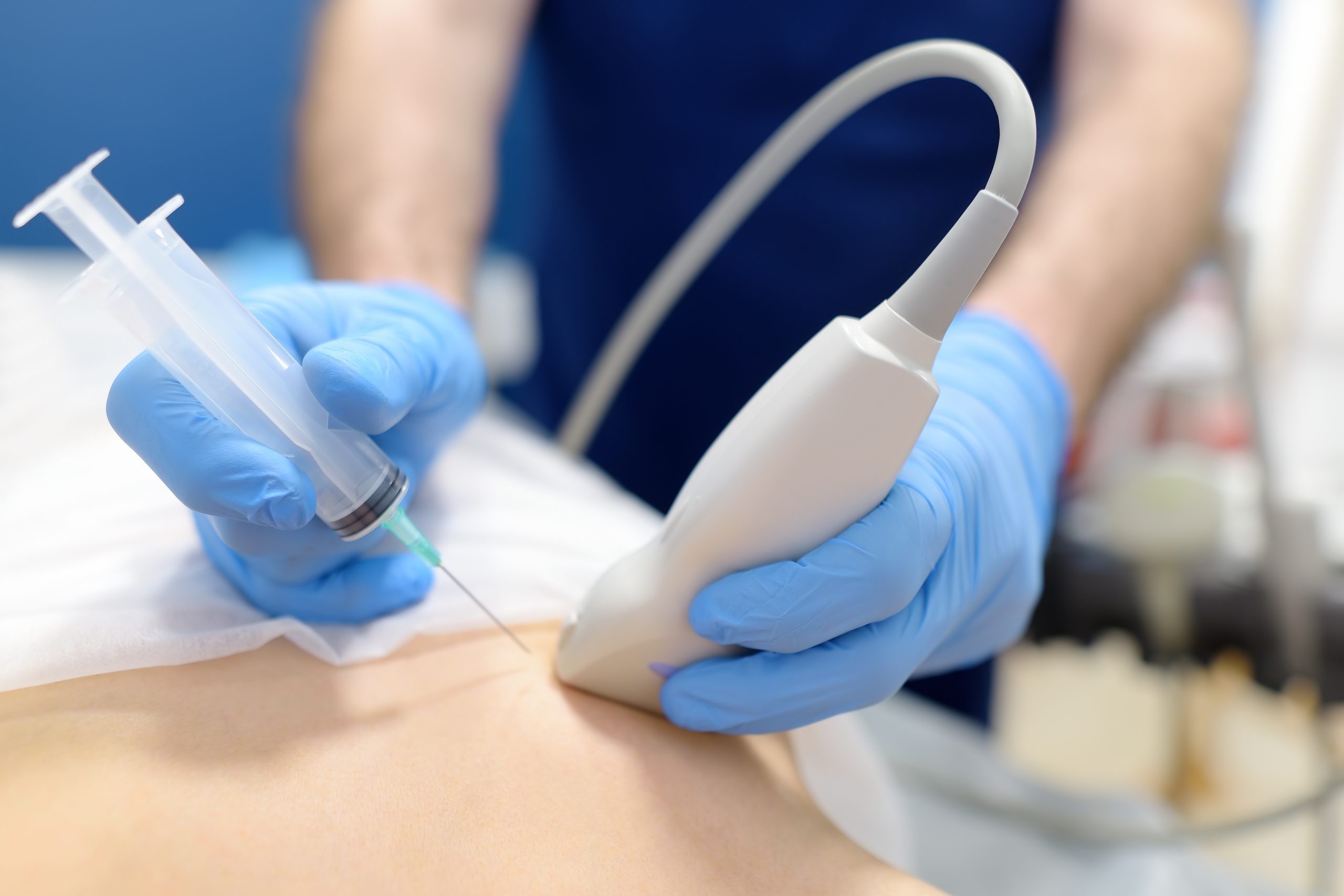
Interventional Radiology provides image-guided techniques for performing biopsies and draining abscesses, offering minimal discomfort and quick recovery compared to traditional methods.
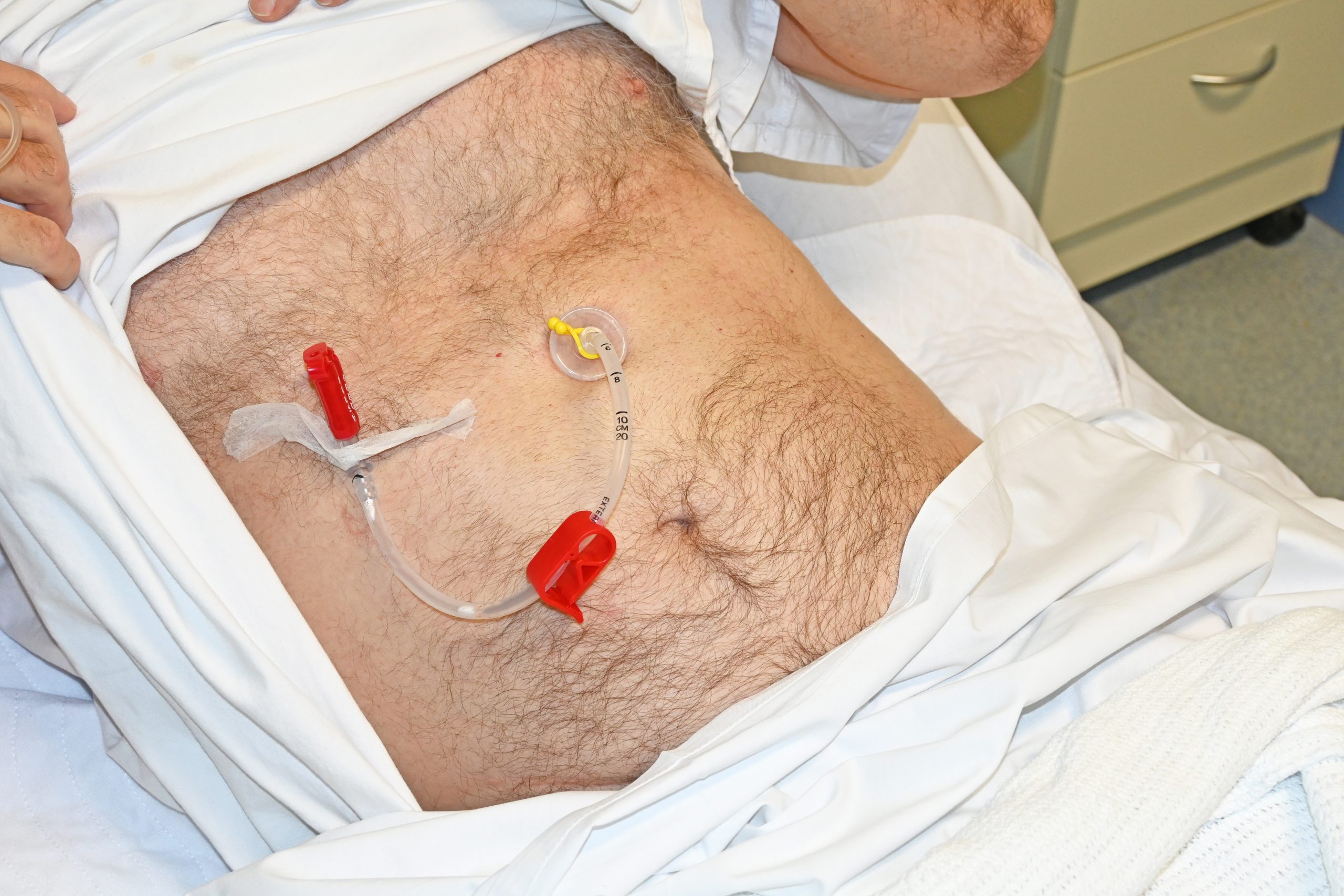
This procedure involves inserting a catheter into the stomach to provide relief from obstructions, facilitating nutrition, digestion and alleviating discomfort.

Minimally Invasive:
Procedures involve small incisions, reducing pain and scarring.
Faster Recovery:
Shorter hospital stays and quicker return to daily activities.
Versatility:
Applicable across various medical conditions and patient profiles.
Reduced Risk:
Lower complication rates compared to traditional surgery.
Targeted Treatment:
Direct delivery of therapy to affected areas, sparing healthy tissues.